- Version
- Download 2534
- File Size 2.70 MB
- File Count 3
- Create Date 30 June 2023
- Last Updated 1 July 2024
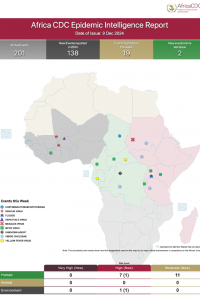
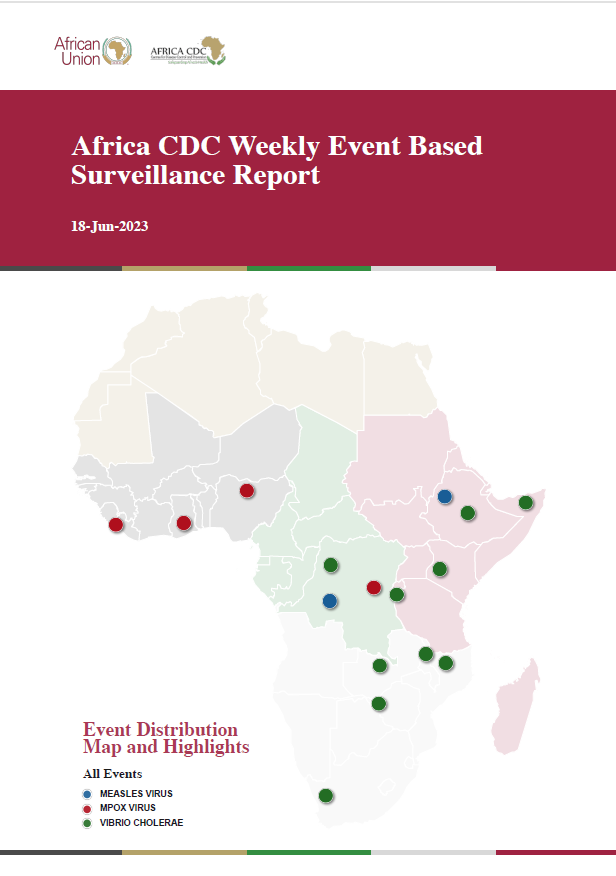
Africa CDC Weekly Event Based Surveillance Report, June 2023
Description:
On 21 May 2023, the Ministry of Health (MoH) of Cote d'Ivoire reported an outbreak of yellow fever. The country has reported oneconfirmed case with no death in Abijan. The case is a 35-year-old male from Cocody-Bengerville sub-prefectures in Abidjan regionwho presented with fever, jaundice, and fatigue symptoms. A confirmatory test was conducted at the Institut Pasteur in Dakar usingpolymerase chain reaction. The yellow fever vaccination status of the case wasn't disclosed.
Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease caused by the yellow fever virus and is transmitted through the bite of infectedAedes mosquitoes. Symptoms include headache, jaundice, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. The overall case fatality ratio(CFR) ranges between 3% to 7.5%. As of August 2022, vaccination coverage for yellow fever in the country was 65%. The lastoutbreak occurred in 2022 with eight confirmed cases and no deaths.
Response:
The MoH continues to conduct active case search and risk communication in the affected region.
Attached Files
| File | Action |
|---|---|
| Africa CDC Weekly Event Based Surveillance Report - 4 June 2023 | Download |
| Africa CDC Weekly Event Based Surveillance Report - 11 June 2023 | Download |
| Africa CDC Weekly Event Based Surveillance Report - 18 June 2023 | Download |